Twin Spacecraft to Weigh in on Earth’s Changing Water
A pair of new spacecraft that will observe our planet’s ever-changing water cycle, ice sheets, and crust is in final preparations for a California launch no earlier than Saturday, May 19.
from NASA https://ift.tt/2jj0v8j
via IFTTT![]()
Ganymede: A Moon Like No Other
Ganymede: A Moon Like No Other
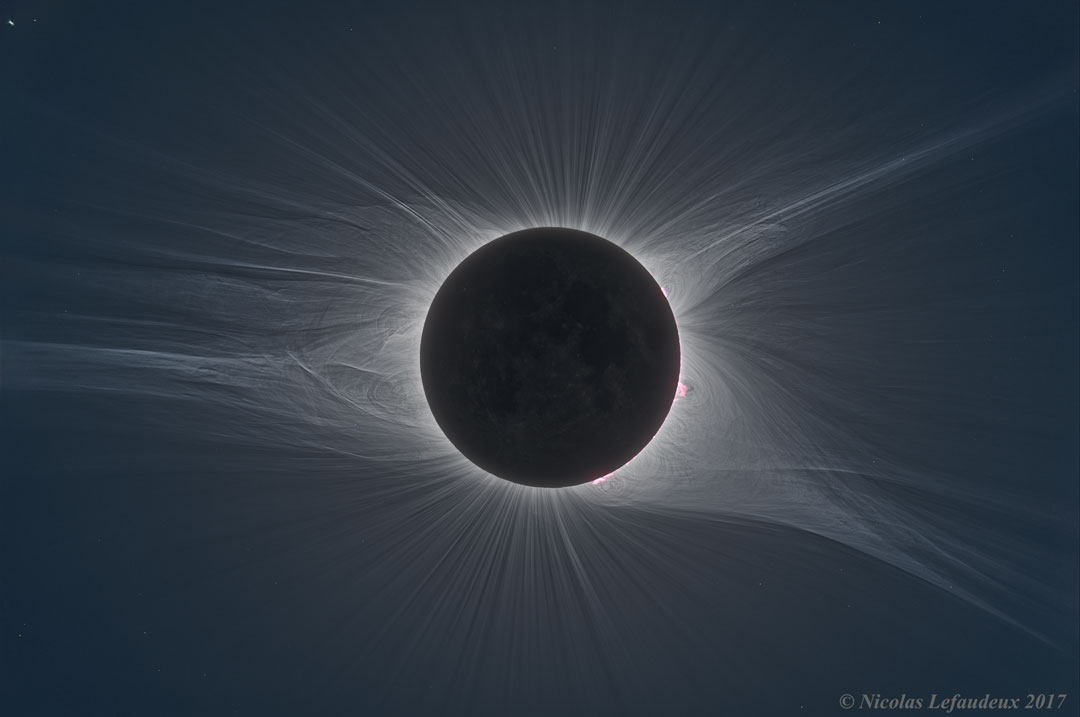
Total Solar Eclipse Corona in HDF

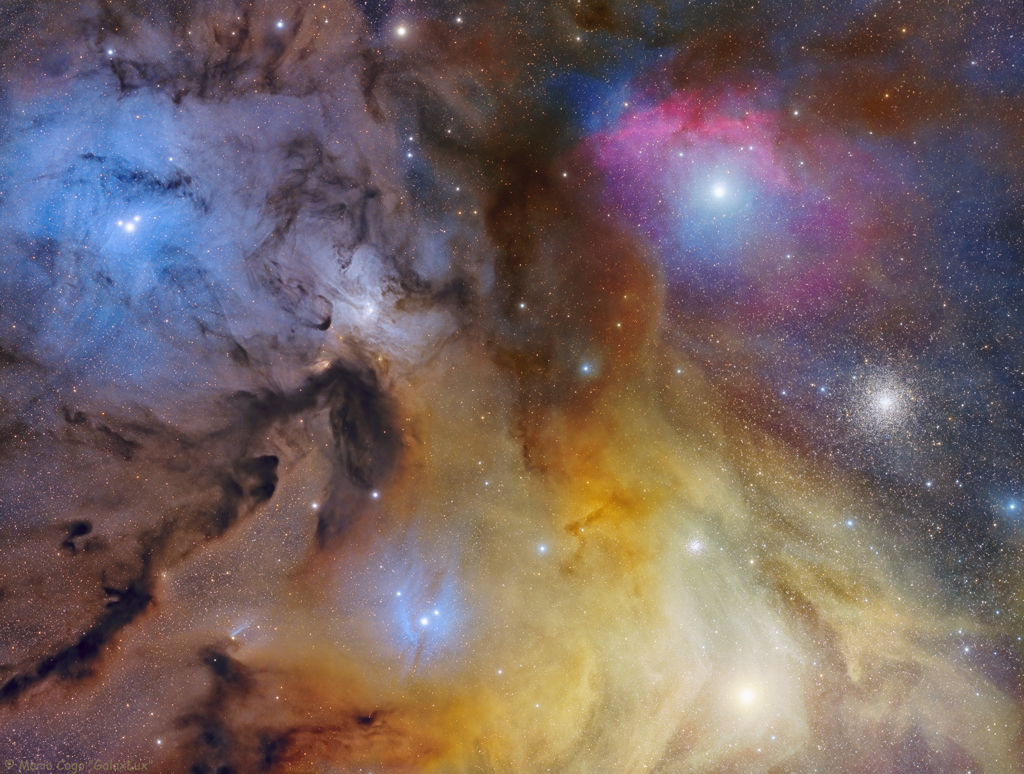
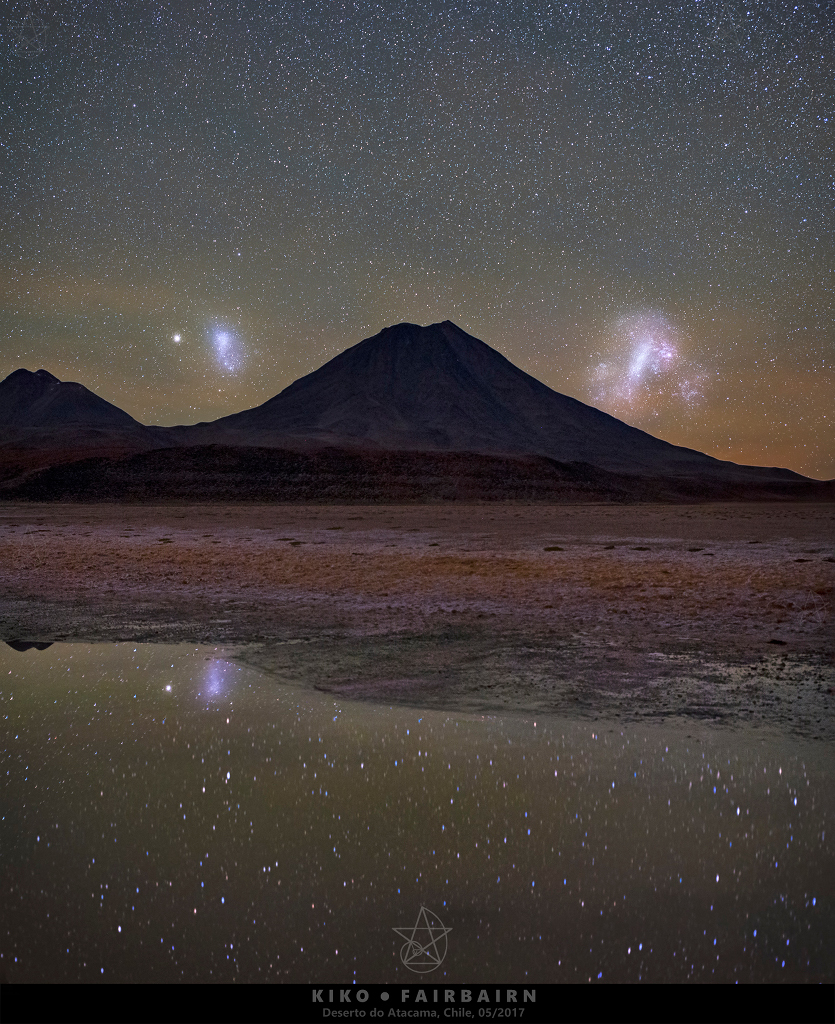
Magellanic Mountain

NASA Sets Sights on May 5 Launch of InSight Mars Mission
NASA’s next mission to Mars, Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight), is scheduled to launch Saturday, May 5, on a first-ever mission to study the heart of Mars. Coverage of prelaunch and launch activities begins Thursday, May 3, on NASA Television and the agency’s website.
from NASA https://ift.tt/2HzYIdy
via IFTTT![]()
Montana, Vermont Students to Speak with NASA Astronauts on Space Station
Students from Montana and Vermont will talk with astronauts on the International Space Station next week as part of NASA’s Year of Education on Station.
from NASA https://ift.tt/2KmwjWq
via IFTTT![]()
Dividing Line
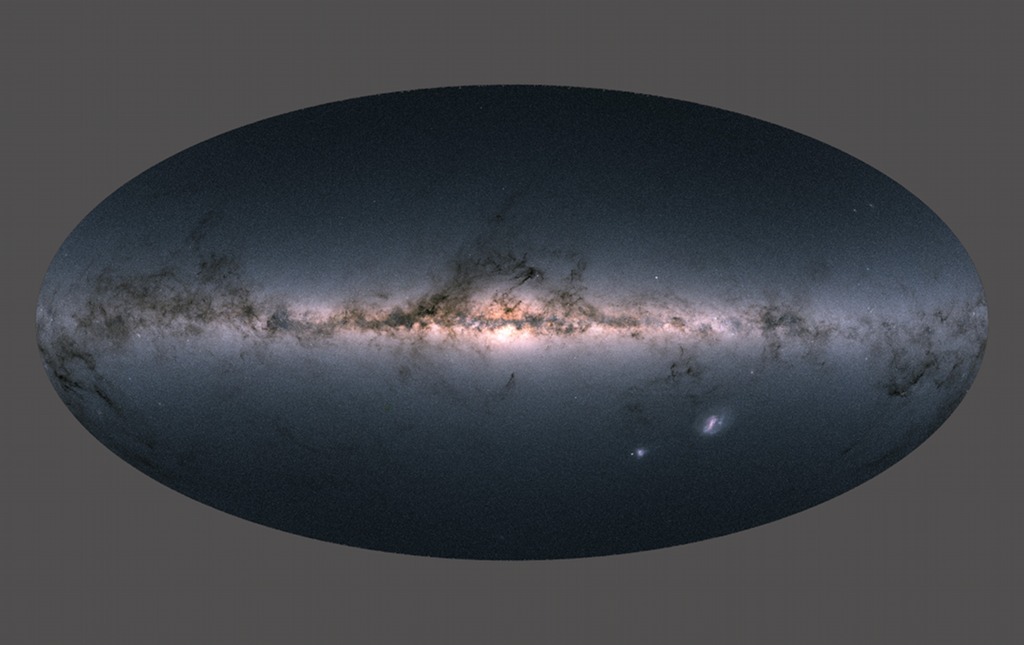
Gaia’s Milky Way